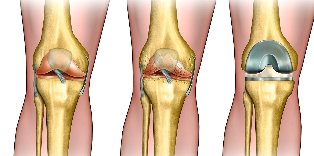
Osteoarthritis – the collective term burned-degenerative disease of the articular cartilage of the apparatus of different localization and aetiology, the similar clinical and morphological picture and the result of the lesion and the articular cartilage, subchondral bone manifested formations, capsule, ligament apparatus.
Osteoarthritis – the most common pathology in rheumatology practice, according to the medical statistics she suffers up to 1/5 of the parts of the population as a whole. Osteoarthritis is disabled cause significant reduction in the quality of life of approximately half of the patients, of which a large part is. The incidence depends on the age: osteoarthritis is rare in young years, made his debut, often after 40-45 years, although in the case of persons older than 70 years of x-ray findings in most cases. At a young age, the incidence of approximately 6.5%, after a 45-year – 14-15%, after 50 years, 27-30%, and individuals older than 70 years – 80% to 90%.
The most common case of arthritis in the pathological process of the small joints of the Hand (in the case of women 10 involved times more often than men), big toe, vertebral joints of the thoracic spine and the cervical parts of the spine, as well as the knee and hip joints. Osteoarthritis of the hip and occupies a leading Position on the degree of severity of the clinical manifestations and the negative impact on the quality of life.
For the arthritis characteristic of the complex lesion of the articular cartilage and Support devices:
- inflammatory changes of the cartilage of the joint;
- through the involvement in the pathological process of the underlying bone structures;
- Synovitis – inflammation of the inner lining of the joint capsule;
- Bursitis lesion of pockets in addition to the joints;
- reactive inflammation of the soft parts (muscles, skin, ligaments), in the projection of the joint.
Since the cause of osteoarthritis inflammatory changes, in a number of Western countries, are commonly referred to as disease Arthritis. In the Russian medicine, the terms Arthritis and osteoarthritis meet as often, and mean one and the same pathological process. In the last time in a rheumatology practice, the most common of the term osteoarthritis is used, the involvement in the pathological process, not only the actual joint, such as mobile connections, but also of his bony formations emphasized.
The consequences of arthrosis in the absence of adequate treatment are a progressive decrease in the mobility of the affected joint immobilization.
Currently, the approach to the understanding of osteoarthritis fundamentally changed: the disease is considered aggressive process of destruction of cartilage tissue of the joint under the influence of inflammation, which requires an active anti-inflammatory therapy.
Synonyms: Arthritis, Osteoarthritis, osteoarthritis, deforming osteoarthritis.
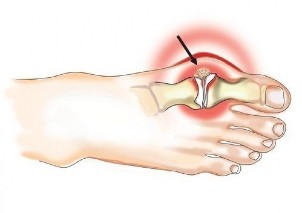
Causes and risk factors
In the scientific community, the controversy over the fundamental causes of the defeat of the joints. Some researchers perform the basic role of a damage of the coating of the cartilaginous joint surfaces under the influence of various factors leads to disruption of the biomechanics of the joint and dystrophic changes in the surrounding structures. Others, however, the cause is seen in the surface layer of the lesion sochlenyayushchihsya bony structures of the joint (for example, by disturbances of the microcirculation), and secondary changes of faith dystrophy and Degeneration of the cartilage.
Causal factors that often provoke the development of osteoarthritis:
- Prior acute traumatic injuries of the joint (rupture or tear of the ligaments, contusions, dislocation, intra-articular fracture, penetrating injuries);
- excessive systematic charge in connection with a particular type of activity (professional athletes, dancers, persons with heavy physical work, etc.);
- Obesity;
- local impacts of low temperatures;
- chronic diseases, in which the local micro-suffers from circulation (endocrine pathology, pathology of the vascular bed occur, etc.);
- migrated acute infectious diseases;
- hormonal changes (pregnancy, menopause);
- Autoimmune diseases require that the damage to the connective tissue;
- connective dysplasia (congenital weakness of this type of material, accompanied by increased mobility of the joints);
- genetic disorder – defective gene, localized on chromosome 12 and the Encoder of procollagen type II (COL2A1) or VDR gene, controlled by the Vitamin D-endocrine System;
- congenital structural and functional abnormalities of the articular cartilage apparatus;
- Mature, elderly and senile age;
- Bone Loss (Osteoporosis);
- chronic intoxication (including alcohol);
- the transferred operative interventions on the joints.
In most cases, osteoarthritis Poly-etiological nature, i.e., the combined effect of multiple causal factors.
Symptoms of osteoarthritis
Not typical for osteoarthritis, acute illness, changes in the joints are moving, slow-growing nature, and a gradual reinforcement of the symptomatology:
- Pain;
- intermittent grinding in the affected joint;
- Deformity of the joint, the emerging and increasing depending on the development of the disease;
- Stiffness;
- Restriction of the mobility (reduction of active and passive movements in the affected joint).
Pain in osteoarthritis is wearing a dull temporary in nature, appears in the movement, on the background of the intensive burden, at the end of the day (can be so intense that it allows the patient to sleep). Constant, non mechanical pain for atypical osteoarthritis and shows the presence of active inflammation (subchondral bone, synovial membrane, ligaments, or periarticular muscles) to be.
The majority of the patients noted the presence of so-called starter-pain in the morning hours after getting up or after a longer time of inactivity, and in the course of the movement activity. A lot of patients to determine the need for, the current state as a "joint evolve" or "diverge".
For osteoarthritis characteristic morning stiffness, which is a significant location and is short (not longer than 30 minutes), sometimes they are perceived by patients as feeling "jelly" in the joints. Perhaps a feeling of Jamming, rigidity.
With the development of reactive Synovitis, the main symptoms of osteoarthritis-align:
- Pain and local increase of the temperature, which on Palpation of the affected joint;
- the constant character of the pain;
- an increase in height of the joint, swelling of the soft parts;
- progressive decrease in the mobility.
For the arthritis characteristic of the rise of the joint in the circumference, swelling of the soft parts.
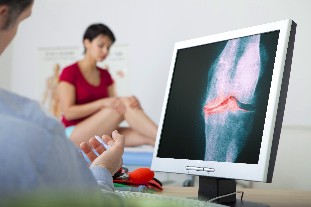
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of osteoarthritis is based on an evaluation of the anamnestic data, the characteristic symptoms of the disease, the results of the instrumental methods of research. Exemplary changes in the General and biochemical analyses of the blood for osteoarthritis are not typical, they appear only in the development of active inflammatory process.
The most important Instrumental method for the diagnosis of osteoarthritis is the x-ray, in diagnostically unclear cases, the implementation of a Computer-or magnetic resonance imaging is recommended.
Osteoarthritis of the hip and occupies a leading Position on the degree of severity of the clinical manifestations and the negative impact on the quality of life.
Other Diagnostic Methods:
- Arthroscopy;
- Ultrasound (assessment of the strength of articular cartilage, synovial fluid, condition of the joint capsules, the presence of the liquid);
- Scintigraphy (a result of the bone condition of the heads of the bone in the joint).
The treatment of osteoarthritis
Drug Therapy:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs – for the relief of pain and signs of inflammation during exacerbation;
- glucocorticosteroid hormones, intra-articular, intravenous introduction to the alleviation of Synovitis phenomena; limits apply in the cases when it is necessary, in the shortest amount of time, the painful symptoms eliminate;
- antifermental agents (inhibitors of proteolysis) – prevents the progression of degenerative and degenerative processes in cartilage and bone tissue;
- Antispasmodics can eliminate local muscle spasms in the damaged Segment;
- anabolic drugs – accelerates the Regeneration of damaged tissue;
- Drugs for the correction of the properties of the blood, strengthening blood vessel walls, increasing the elasticity and tissue regeneration – contribute to the strengthening of the walls of the blood microcirculatory bed vessels, allowing adequate blood supply to the injured area;
- Tools, improving microcirculation;
- Medication for the joints, in spite of their mass distribution in the therapy of Arthritis, in large Placebo-controlled trials demonstrated the clinical efficacy of this group of drugs.
Physiotherapy techniques applied for the treatment of osteoarthritis:
- Massage regional muscles, improves blood circulation and relieves the local spasm;
- active physiotherapy, that is, the execution of the exercises for osteoarthritis with the help of special simulators;
- Physiotherapy for osteoarthritis;
- Laser therapy;
- Ultrasonic Treatment;
- medical baths, mud, Paraffin, etc.
The ineffectiveness of the above-mentioned methods of influence, handle in the presence of complications to the surgical treatment of osteoarthritis:
- The decompression of meta-epiphysis and extended within the bony blockages (reduction of intraosseous pressure in the affected area);
- corrective osteotomy;
- Arthroplasty of the joints.
In the early stages of the disease, mechanical, laser device (smoothing the surface of cartilage damage, removal of devitalized phases). This method effectively pain relieves syndrome, but of temporary effect – go for 2-3 years.
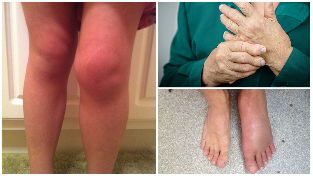
Possible complications and consequences
The consequences of osteoarthritis, especially in the absence of adequate treatment are:
- Progressive reduction of the mobility in the affected joint;
- Immobilization.
Prediction
Prognosis for life. Effective social and employment prognosis depends on the timeliness of diagnosis and beginning of treatment, is reduced when tightening the solution of the question of surgical treatment of the disease in case of need.
Prevention
- Refusal of intense stress, prolonged static tension of the affected joint.
- The wearing of orthotics, if necessary.
- The diet for osteoarthritis for the reduction of body weight.
- Prevention of hypothermia.
- Holistic treatment of acute injuries to the joints until full recovery with the mandatory rehabilitation.
- Clinical examination in case of signs of osteoarthritis.


































