Thoracic osteochondrosis is a chronic disease, in the basis of the degenerative-dystrophic lesions of the intervertebral cartilage-drive, leading to reactive changes on the part of the body of the vertebra and the surrounding soft parts. The disease is widespread and affects primarily people of working age (25-45 years).
Thoracic osteochondrosis occurs much less frequently than lumbar or cervical. This is due to the fact that this division of the spine falling of the smaller static and motor load, than others. However, osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is much more difficult to diagnose, as it in most cases, the Simulation of diseases of the lung, the heart, the organs of the upper section of the digestive system runs.
Causes and risk factors
Currently, the exact causes for the emergence of thoracic osteochondrosis are not installed. Experts asked a variety of theories (infectious-allergic, genetic, mechanical, hormonal, vascular), but none of them will not transmit a clear and full explanation of the pathological changes in the spine and leads to a Degeneration of the tissue. Probably in one of the pathological Mechanisms of the chest of drawers osteochondrosis at the same time a plurality of different factors is involved. But the main importance belongs to a long static-dynamic overloads vertebral Segment.
Factors such overload:
- abnormal structure of the spine;
- asymmetrical arrangement of the columns in the joint intervertebral joints;
- congenital narrowing of the spinal canal;
- spondylogenic muscle (myofascial reflected) and/or somatic (reflected, vessels on the background of a number of diseases of the blood and the internal organs) pain;
- prolonged exposure to vibration on the spine, for example, in the case of drivers of motor vehicles;
- physical stress;
- Obesity;
- Smoking;
- a sedentary (lack of exercise) life;
- psycho-social factors.
The mobility of the spine by intervertebral discs that play well and dampen roll. In the middle of an elastic gelatinous core, the composition of which contain large quantities of water. In the case of the osteochondrosis of the core, the water loses through the desalination of polysaccharides. With the time the core is flattened, and with it flattened, and even the intervertebral disc. Under the influence of mechanical stress on the fiber ring buckles, this process is called the projection. Later in the disc cracks, the fragments of the liquid ring and the nucleus pulposus, i.e., the formation of the intervertebral disc prolapse.
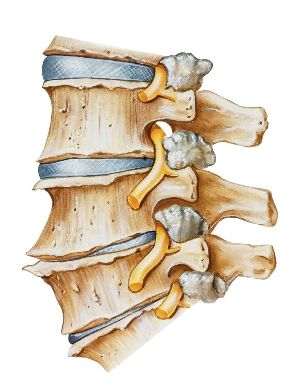
The reduction of the disc height leads to an approximation of the adjacent vertebrae, disruption of the anatomy of the vertebral joints. All of this leads to reactive inflammation of the facet joints and the surrounding soft parts. Apart from that, the approach of the vertebral body and elongation of the joint accompanied capsules, and the affected Segment of the spine becomes unstable. The vertebral body caused by excessive mobility, the roots of the cause for the impairment of the spinal and the arrangement of the edge of the development of the syndrome.
On the background of osteochondrosis gradually, the bone tissue of the vertebral body grows and forms the bony outgrowths (osteophytes). You can also cause the arrangement of the rim of the occurrence of the syndrome or myelopathy (compression of the spinal cord).
Classification
The basis of the classification of thoracic osteochondrosis is posindromnoy principle. Depending on the affected nerve structures of the spine, there is the following Syndrome:
- Compression fitting base in its development is the tension, the deformation or compression of the nerve root, the Phase of the spinal cord or the blood vessel, depending on what develop spinal, vascular or radicular syndromes;
- Reflex – through associated with Reflex voltage of the innervated muscles, degenerative, and circulatory disorders;
- bioadaptive.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis of thoracic spine
The primary Symptom of thoracic osteoarthritis of the pain. In most cases, she wears a dull light in nature.
Prolonged irritation of the spinal nerve roots to disorders of Innervation of the internal organs. Depending on the extent of the destruction, Thoracic osteochondrosis leaking under the mask of somatic pathologies can:
| The level of defeat | The innervated organs | Clinical Symptoms. |
| C7-Th1 | Hands, Wrists, Hands, Trachea, Esophagus | Pain in the hands and the palms of the hands, bronchial Asthma |
| Th2-Th3 | Heart, Pericardium, Coronary Arteries | Coronary Heart Disease, Heart Rhythm Disorders |
| Th4-Th5 | Bronchi, Lungs, Pleura, Chest Of Drawers, Nipples | Bronchitis, Pneumonia, Pleurisy>[!@#$], Bronchial Asthma |
| Th5-Th6 | The bile duct, the gallbladder | Jelchnokamennaya disease, disorder, and Absorption of fats |
| Th6-Th7 | Liver, Solar Plexus | Liver function disorders |
| Th7-Th8 | Stomach | Dyspepsia, Gastritis, ulcers disease stomach and duodenal |
| Th8-Th9 | Duodenum, Pancreas | Digestive disorders, and chair, Duodenitis, pancreatitis |
| Th9-Th10 | Spleen, Diaphragm | Hiccup, diseases of the respiratory tract |
| Th10-Th11 | Adrenal | Allergic reactions, decreased immunity |
| Th11-Th12 | Kidney | Pyelonephritis, Urolithiasis |
| Th12-L1 | Kidney and ureter | Disorders of bladder emptying |
In this context, the most common symptoms of the thoracic spine degenerative disc disease:
- Pain in the chest (behind the breastbone, in the side, the back, the intercostal space in between) – can be so sharp, and so worn, blunt; often radiating to the arm;
- Pain in the upper abdomen – is the same irrespective of the type of diet, characteristics of diet; often combined with heartburn, nausea, vomiting;
- Pain in the right hypochondrium – amplified in the change of the body position of the patient, sneezing, cough;
- Pain in the lumbar area – mimic attack of renal colic, often combined with dysuric disorders.
In the case of compression of the nerve root in a patient with thoracic osteochondrosis attack developed by intercostal neuralgia. It's characterized by the occurrence of acute pain in one half of the Thorax (torakalgiya) is. Pain-Herpes-character are sensations and extend along one of the intercostal nerves from the spine to the sternum. Patients describe it as "the effect of electric current" or "lumbago". To give the pain in the epigastrium, retrosternal area, shoulder blade, arm, and go with some other symptoms (local hyperhidrosis, pallor or redness of the skin), in connection with a lesion of the sympathetic fibers intercostal nerves.
For intercostal neuralgia characteristic of painful attacks over a period of a few seconds up to several minutes. During the attack, the pain will become unbearable. Tried somehow to ease your condition, the patients to freeze in a certain Position of the body, avoiding deep breaths, coughing, sneezing, twists and turns.
Outside of the pain-attack tingling in patients with paresthesia (subjective disorders of the skin sensitivity in the Form of crawling, tickling, tingling, needles) along the intercostal space.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of thoracic osteochondrosis is carried out on the basis of data of the physical examination of the patient, laboratory and Instrumental examination, including:
- The blood picture (moderate leukocytosis, increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate);
- Serum electrolytes (reduction in the level of calcium);
- the General analysis of urine;
- biochemical analysis of blood;
- X-ray examination of the thoracic spine (detectable flattening of the intervertebral disc, the deformation of the closing plates of the adjacent vertebral bodies, Tel displacement of adjacent vertebrae to each other);
- Scintigraphy of the spine (bringing the active process of mineralization of the bone tissue of the vertebral body);
- Myelography;
- Computer and magnetic resonance tomography.
Thoracic osteochondrosis requires differential diagnosis with the following diseases and pathological States:
- dishormonal spondylopathy;
- Spondylolisthesis;
- inflammatory processes;
- ankylosing Spondylitis;
- Osteomyelitis of the spine;
- rheumatoid Arthritis;
- neoplastic processes (metastases or primary tumors of the breast);
- Fractures of the spine;
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (chronic pancreatitis, ulcers disease stomach and duodenal ulcers, diverticulitis, irritable bowel syndrome);
- Diseases of the genitourinary system (Urolithiasis, Pyelonephritis);
- Cardiovascular diseases (coronary heart disease, heart rhythm disorders).
The treatment of the osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine
Treatment of thoracic degenerative disc disease is performed on an outpatient basis. When expressed pain syndrome patients for 2-3 days, prescribe bed rest. Shows the traction that the affected Segment of the spine, which releases the compression of the nerve root and therefore pain. When expressed pain syndrome lead to the Infiltration of the soft parts of a 2% solution of novocaine. In the short space assigned to steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can not be, -.
In the scheme of complex treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis are also included:
- Antihistamines;
- B-Vitamins;
- Tranquilizers;
- Acupuncture;
- Massage;
- the manual therapy.
After the improvement of the condition of the patient is exercises on the physiotherapy. Regular exercise in osteochondrosis promotes the formation of well-developed muscular corset, the the spine keeps to hold in the correct physiological state, eliminates unwanted static charges.
The non-negligible role in the treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis relegated to regular moderate physical exercise (swimming, Yoga, Tai-Chi), the normalization of body weight. Jumping, running, weight lifting and other sports, accompanied by increased loads on the spine, is contraindicated.
Surgical treatment of breast osteochondrosis shows only in the event of a significant compression of the spinal cord. In such cases, depending on the indication, continue:
- Stabilization of vertebral body-Segment;
- Replacement of the affected disk artificial implant;
- Laser reconstruction of the hard disk;
- Puncture evaporation of the affected disk;
- micro discectomy.
Possible consequences and complications
Prolonged irritation or compression of a nerve root may be kidney development of somatic diseases of organs in the chest, the upper section of the digestive system, the. The biggest risk of Thoracic osteochondrosis is for infarction.
Also, the impact of the commode arthritis be able to to diseases of esophagus, stomach, duodenum, pancreas, gall-bladder, the lungs, the formation of a hernia.
Prediction
Thoracic osteochondrosis is characterized by a wavy current at which the Remission accompanied by exacerbations. The time started to treatment, compliance with all recommendations of the doctor by the patient, both in terms of the treatment of diseases and lifestyle changes, the prognosis is favorable.
Prevention
Prevention of breast degenerative disc disease includes:
- Normalization of body weight;
- Smoking cessation;
- an active life style.


































